Effective Strategies for Aligning EBITDA Expectations with Reality

In our previous blog titled “From Expectations to Reality: Understanding EBITDA Variations”, we delved into the intricacies of EBITDA variations., “From Expectations to Reality: Understanding EBITDA Variations,” In this subsequent blog, we aim to equip you with the approaches to improve your business’s profitability proactively.
A recent survey from Deloitte suggests that 82% of companies said they missed their cost-reduction targets, up from 72% a year ago. This is the highest failure rate Deloitte has ever recorded since starting this series in 2008 (Source: Deloitte)
The Approach for Bridging the Gap
83% of companies are looking to change how they run their business margin improvement efforts (Source: Deloitte)
This section will outline the strategies to align your business with EBITDA expectations and transform them into tangible realities.
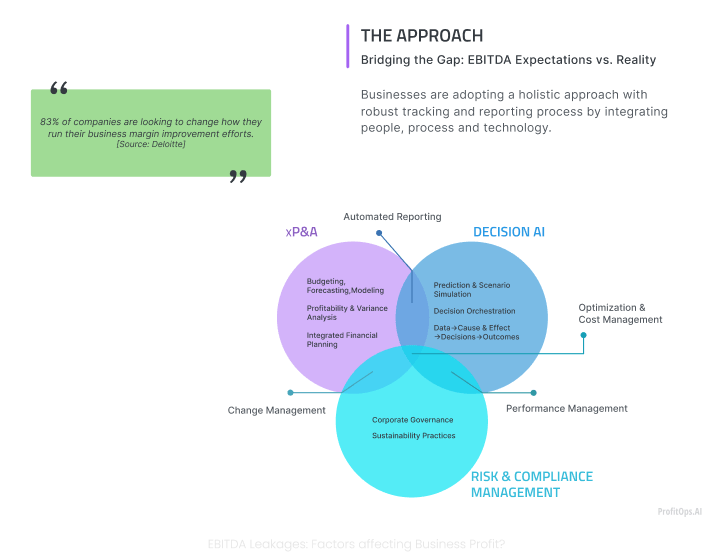
Businesses are adopting a holistic approach with robust optimization & cost management processes by integrating people, processes, and technology that incorporates the following:
- xP&A:
Cross-functional Planning and Analysis (xP&A) is a comprehensive process encompassing budgeting, forecasting, financial modeling, profitability analysis, variance analysis, and Integrated Financial Planning. Budgeting entails developing detailed financial plans for a fiscal year while predicting, which involves revising financial projections based on the latest data. xP&A leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to update forecasts. Financial modeling simulates various scenarios and assesses potential outcomes. Profitability Analysis evaluates the profitability of business segments, while Variance Analysis compares actual performance with budgets or forecasts. Integrated Financial Planning aligns financial planning with strategic and operational planning to ensure coherence with business strategy and operational plans.
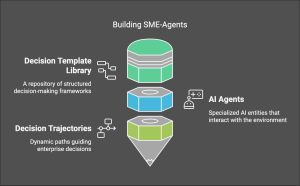
- Decision AI:
- Risk and Compliance Management :
The alignment of Risk and Compliance Management with corporate governance and sustainability practices significantly enhances the overall efficacy and dependability of an organization’s planning and performance management processes. By integrating Decision AI and change management into Extended Planning and Analysis (xP&A), organizations can more effectively attain their performance management objectives. The integration of corporate governance frameworks ensures that decision-making processes adhere to legal requirements, ethical standards, and best practices, thereby enhancing transparency, accountability, and integrity within the organization. The inclusion of ESG criteria in risk management practices enables organizations to consider environmental and social impacts alongside financial performance, thereby promoting sustainable business practices and bolstering corporate reputation. Implementing sustainability practices involves efficient resource management, waste reduction, and minimizing environmental impact, contributing to long-term operational efficiency and resilience.
Evolution of xP&A and Decision AI Tools
85 percent of business leaders have suffered from decision distress, 93 percent believe having the right type of decision intelligence can make or break the success of an organization. (Source: Oracle)
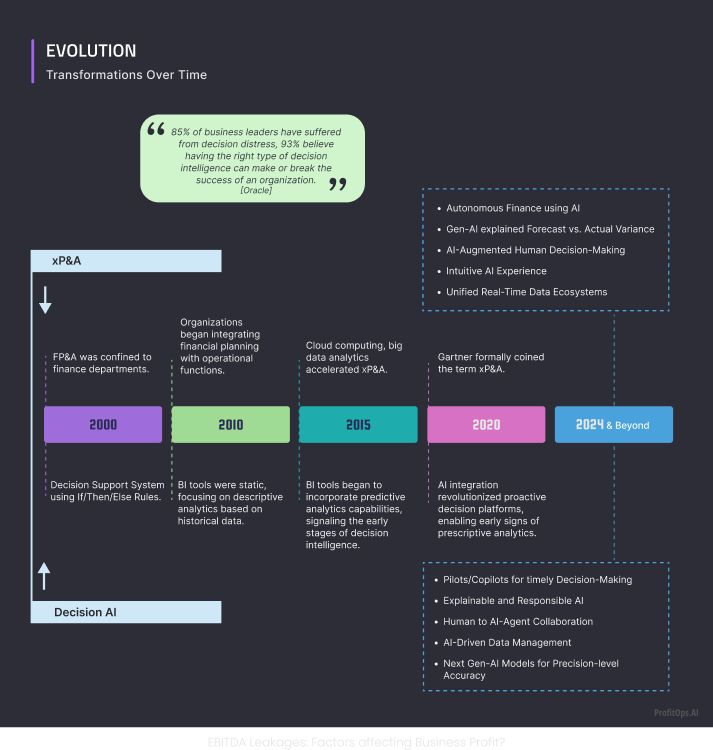
- Evolution of xP&A
2000 – FP&A was confined to finance departments. (Source: SAP)
2010 – Organizations began integrating financial planning with operational functions. (Source: Insightsoftware)
2015 – Cloud computing and big data analytics accelerated XP&A. (Source: SAP)
2020 – Gartner formally coined the term xP&A. (Source: Gartner Research)
2024 and beyond – Autonomous Finance using AI, Gen-AI driven Forecast and Budget Variance Explanation, AI-Augmented Human Decision-Making, Intuitive AI Experience Unified Real-Time Data Ecosystems. (Source: Financealliance)
- Evolution of Decision AI Tools
2000 – Decision Support System using If/Then/Else Rules. (Source: Lawrence University)
2010 – BI tools were static, focusing on descriptive analytics based on historical data. (Source: SAP)
2015 – Bl tools began incorporating predictive analytics capabilities, signalling the early stages of decision intelligence. (Source: Spiceworks)
2020 – AI integration revolutionized proactive decision platforms, enabling early signs of prescriptive analytics. (Source: Cubesoftware)
2024 and beyond educated projections- Pilots/Copilots for timely decision making, Explainable and Responsible AI, Human-AI Agent Collaboration, AI-Driven Data Management, Next Gen-AI Models for precision-level accuracy. (Source: Financealliance)
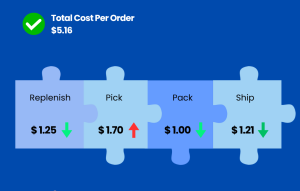
Example Scenario of addressing EBITDA variances
CEO to CFO: “Hi, do you have any recommendations on how we can improve the gross margin on shoe sales for the next quarter?”
In addressing the CEO’s question, the approaches of Company-A utilizing Next Gen xP&A with Decision AI and Company-B leveraging ERP systems and spreadsheets would likely differ significantly due to their respective strengths and toolsets.
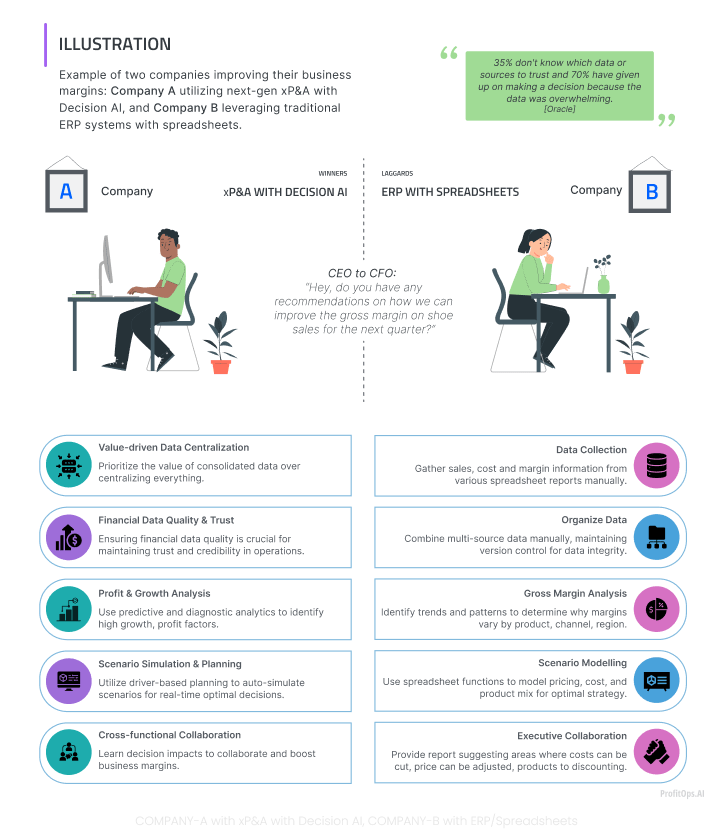
- Company-A: xP&A with Decision AI
Company-A’s approach would leverage value-driven data centralization, financial data quality & trust, profit & growth analysis, scenario simulation & planning and cross-functional collaboration :
- Value-driven Data Centralization: Prioritize the value of consolidated data over centralizing everything.
- Financial Data Quality & Trust: Ensuring financial data quality is crucial for maintaining trust and credibility in operations.
- Profit & Growth Analysis: Use predictive and diagnostic analytics to identify high-growth profit factors
- Scenario Simulation & Planning: Use driver-based planning to auto-simulate scenarios for optimal real-time decisions.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Learn decision impacts to collaborate and boost business margins.
- Company-B: ERP with Spreadsheets
Company-B’s approach would likely be conventional, emphasizing extensive financial analysis and meticulous manual data scrutiny, covering
- Data Collection: Manually gather sales, cost and margin information from various spreadsheet reports.
- Organize Data: Combine multi-source data manually, maintaining version control for data integrity.
- Gross Margin Analysis: Identify trends and patterns to determine why margins vary by product, channel, and region.
- Scenario Modelling: Use spreadsheet functions to model pricing, cost, and product mix for optimal strategy.
- Executive Collaboration: Provide a report suggesting areas where costs can be cut, prices can be adjusted, and products can be discounted.
Company-A leverages automated, data-driven insights and predictive models to quickly identify issues and suggest improvements, while Company-B uses traditional, thorough, and somewhat manual financial analysis to provide strategic recommendations. Company-A’s approach may be faster and more adaptable to changing conditions, but it may be less rooted in the extensive, contextual business understanding that a traditional FP&A team might provide. On the other hand, Company-B’s methods, while slower, are likely to produce detailed, actionable financial insights rooted in established analytical practices..
35 percent don’t know which data or sources to trust and 70 percent have given up on making a decision because the data was overwhelming.(Source: Oracle)
Call To Action
99% of surveyed executives are planning to implement some form of business margin improvement program. (Source: Deloitte)
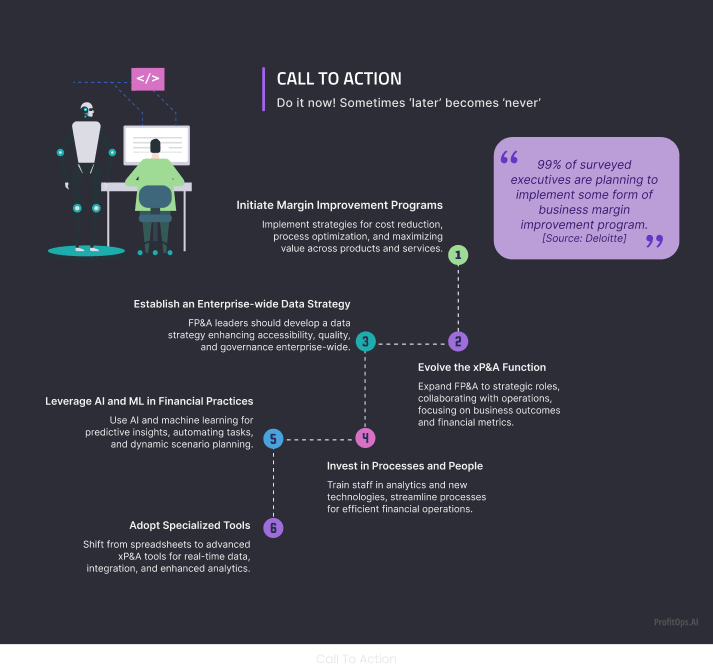
- Initiate Margin Improvement Programs:
Implement strategies for cost reduction, process optimization, and maximizing value across products and services. (Source: Beacon CFO plus)
- 0Evolve the xP&A Function:
Expand FP&A to strategic roles, collaborating with operations and focusing on business outcomes and financial metrics. (Source: FP&A Trends)
- Establish an Enterprise-wide Data Strategy:
FP&A leaders should develop a data strategy enhancing accessibility, quality, and governance enterprise wide. (Source: Infopulse)
- Invest in Processes and People:
Train staff in analytics and new technologies and streamline processes for efficient financial operations. (Source: Strategileadership)
- Leverage AI and ML in Financial Practices:
Use AI and machine learning for predictive insights, automating tasks, and dynamic scenario planning. (Source: Veritis)
- Adopt Specialized Tools:
Shift from spreadsheets to advanced xP&A tools for real-time data, integration, and enhanced analytics. (Source: IBM)
Summary
In summary, organizations must accurately align their EBITDA expectations with reality to optimise their financial performance. Achieving this alignment requires implementing effective strategies that promote informed decision-making. By adopting these strategies, organizations can enhance their ability to make sustainable financial decisions and achieve long-term success.
In our upcoming blog post, we will explore the various types of artificial intelligence (AI) that can be leveraged to boost profitability, focusing on their applicability to business professionals. This discussion will delve into the practical applications of AI in different industries, highlighting how AI has been used to optimize business operations and enhance decision-making processes.
References:
- Rethinking business margin improvement strategies
- Innovation Insight for Extended Planning and Analysis (xP&A)
- Global Study: 70% of Business Leaders Would Prefer a Robot to Make Their Decisions
Shravan Talupula
Founder, ProfitOps